Remoscope: a label-free imaging cytometer for malaria diagnostics Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2025
|
 IL-6 underlies microenvironment immunosuppression and resistance to therapy in glioblastoma bioRxiv, 2025
|
 A Trypanosoma cruzi Trans-Sialidase Peptide Demonstrates High Serological Prevalence Among Infected Populations Across Endemic Regions of Latin America medRxiv, 2025
|
 Proteomic profiling of the local and systemic immune response to pediatric respiratory viral infections American Society for Microbiology, 2025
|
 Endogenous antigens shape the transcriptome and TCR repertoire in an autoimmune arthritis model The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2024
|
 Unveiling the proteome-wide autoreactome enables enhanced evaluation of emerging CAR T cell therapies in autoimmunity J Clin Invest 2024
|
 Total Syntheses of Cyclomarin and Metamarin Natural Products Organic Letters, 2024
|
 Anti-RGS8 paraneoplastic cerebellar ataxia is preferentially associated with a particular subtype of Hodgkin's lymphoma Springer Nature, 2024
|
 Microbial dynamics and pulmonary immune responses in COVID-19 secondary bacterial pneumonia Nature Portfolio, 2024
|
 Climate, demography, immunology, and virology combine to drive two decades of dengue virus dynamics in Cambodia PNAS, 2024
|
 Molecular mimicry in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children Nature Portfolio, 2024
|
 Phage Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing Reveals CDHR5 Autoantibodies in Select Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease American College of Rheumatology, 2024
|
|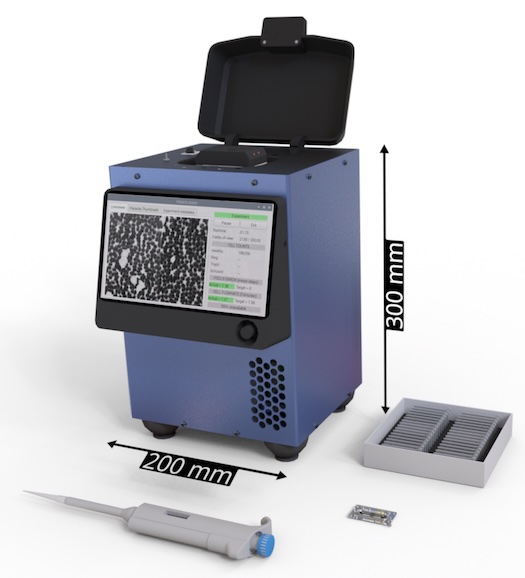  Check out the latest from the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub SF: The Remoscope - an affordable device that leverages edge compute AI for the rapid diagnosis of blood infections, in this case with malaria. This device can process and analyze approximately 2 million cells in 12 minutes, using only finger-prick amounts of blood, with no staining or fixation, and without an internet connection. Staining parasites followed by manual examination and counting with a microscope has been the gold standard for over 100 years. The Remoscope removes the need for time consuming processing of slides, as well as the inherent variability of human counters. As a malaria researcher, this has been a personal dream for decades. Importantly, the Remoscope detects live parasites, unlike PCR assays or lateral flow assays. In this paper, the Remoscope was deployed in the field for true head-to-head comparisons of performance. At its heart, the Remoscope is an imaging flow cytometer with built in AI image processing. As such, the Remoscope may be trained to recognize not just parasites, but other abnormalities in the blood, making it a versatile platform for interrogating blood samples without specialized reagents. Hats off to the amazing Bioengineering team at the CZ Biohub SF. Check out the paper here! Read the paper here. |
 While children were largely spared during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, is one of the enduring mysteries of the early years of COVID. MIS-C manifests as a severe post-COVID inflammatory syndrome affecting multiple organ systems and often requires extreme measures of life support. Despite numerous investigations, the underlying drivers of MIS-C for the majority of cases remained unclear.
In close collaboration with numerous laboratories and clinicians across the country, including the , Baylor, Univ. of Mississippi, Emory, Univ of Alabama at Birmingham, Univ. of Pennsylvania, Nicklaus Children’s Hospital, Univ. of North Carolina Chapel Hill, Univ. of Utah, Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, Indiana University, Children’s Mercy Kansas City, Vanderbilt, Cooperman Barnabas Medical Center, Univ. of South Carolina Charleston, Univ. of Colorado, the CDC, St. Jude Children’s Hospital, and UCSF, we report a significant breakthrough that sheds light on the origins of this severe disease.
Read the paper here. |
|